What Is a Collections Framework?
A collections framework is a unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections. All collections frameworks contain the following:
- Interfaces
- Implementations
- Algorithms
Benefits of the Java Collections Framework
- Reduces programming effort: By providing useful data structures and algorithms, the Collections Framework frees you to concentrate on the important parts of your program rather than on the low-level “plumbing” required to make it work.
- Increases program speed and quality: This Collections Framework provides high-performance, high-quality implementations of useful data structures and algorithms.
Collection Interfaces:
The core collection interfaces encapsulate different types of collections, which are shown in the figure below.
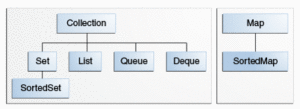
Collection— Root of the collection hierarchy. TheCollectioninterface is the least common denominator that all collections implement. Some types of collections allow duplicate elements, and others do not.Set— A collection that cannot contain duplicate elements.List— An ordered collection.Listcan contain duplicate elements.Queue— A collection used to hold multiple elements prior to processing. Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO (first-in, first-out) manner.Deque— A collection used to hold multiple elements prior to processing. Deques can be used both as FIFO (first-in, first-out) and LIFO (last-in, first-out). In a deque all new elements can be inserted, retrieved and removed at both ends.Map— An object that maps keys to values. AMapcannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value.
The last two core collection interfaces are merely sorted versions of Set and Map:
SortedSet— ASetthat maintains its elements in ascending order.SortedMap— AMapthat maintains its mappings in ascending key order.
This was just an overview, I will be covering each Interfaces and its implementation in upcoming posts marked under Collections category. Stay Tuned…
0 Comments