Overview
In this blog, we will cover following points
- What is IoC
- Spring IoC Container
- Dependency Injection in Spring
- Example Code
Inversion of Control(IoC)
- Inversion of Control is a principle in software engineering by which the control of objects or portions of a program is transferred to a container or framework.
- Inversion of Control can be achieved through various mechanisms such as: Strategy design pattern, Service Locator pattern, Factory pattern, and Dependency Injection (DI).
Spring IoC Container
- The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container.
- The BeanFactory interface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object. ApplicationContext is a sub-interface of BeanFactory.
- The interface org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext represents the Spring IoC container and is responsible for instantiating, configuring and assembling objects known as beans, as well as managing their lifecycle.
- The container gets its instructions on what objects to instantiate, configure, and assemble by reading configuration metadata.
- The configuration metadata is represented in XML, Java annotations, or Java code.
- The Spring framework provides several implementations of the ApplicationContext interface — ClassPathXmlApplicationContext and FileSystemXmlApplicationContext for standalone applications, and WebApplicationContext for web applications.
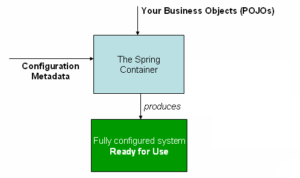
Spring IoC container
Sample Context Code
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Dependency Injection (DI) in Spring
- To set the address attribute in the example above, we can use metadata.
- Then, the container will read this metadata and use it to assemble beans at runtime.
- Dependency Injection in Spring can be done through constructors, setters or fields.
Example
- In this example, we will try to understand IoC and DI.
- sampleContext.xml will contain metadata for Spring Container to Configure at runtime.
- Paint is interface and RedPaint is its implementation class.
- We will define this class as Bean so that we can use it wherever we want.
sampleContext.xml
Paint.java
RedPaint.java
MainApp.java
- When MainApp is executed.
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext will look for sampleContext.xml in classpath.
- This part is reading Configuration Metadata in Spring IoC container image above.
- If you see OUTPUT RedPaint Constructor called is called before Configuration Loaded Successfully
- What this means is Spring Container will see what meta definition we have defined and load that for us ie Constructing Paint Object for us.
- Now our Bean is ready to use we can get it from Context using Bean Name defined in XML and use accordingly.
Note: Above example is build as Java Project. You can download Code from here. I have added Spring Dependent Jars into Classpath after downloading them from here.
Summary
- Inversion of Control (IOC) and Dependency Injection (DI) are used interchangeably.
- IOC is achieved through DI. DI is the process of providing the dependencies and IOC is the end result of DI.
0 Comments